Knowledge Product: A tangible output (document, service, event, media, etc) of prepared knowledge that enables action of selected users. The preparation of knowledge is the process that collects, manages, and shares knowledge in a certain manner. KP is a tool developed that enables interconnectivity between people, information, and processes. It can also support visual tools aimed at achieving strategic learning goals.
The knowledge product serves as a basis for extracting knowledge sharing products available to fit different users, so they should have some attributes in common: attractiveness, value, monitoring, sustainable, scalability (e.g. adaptable within existing systems architecture) and actionable (e.g. trigger actions).
Content
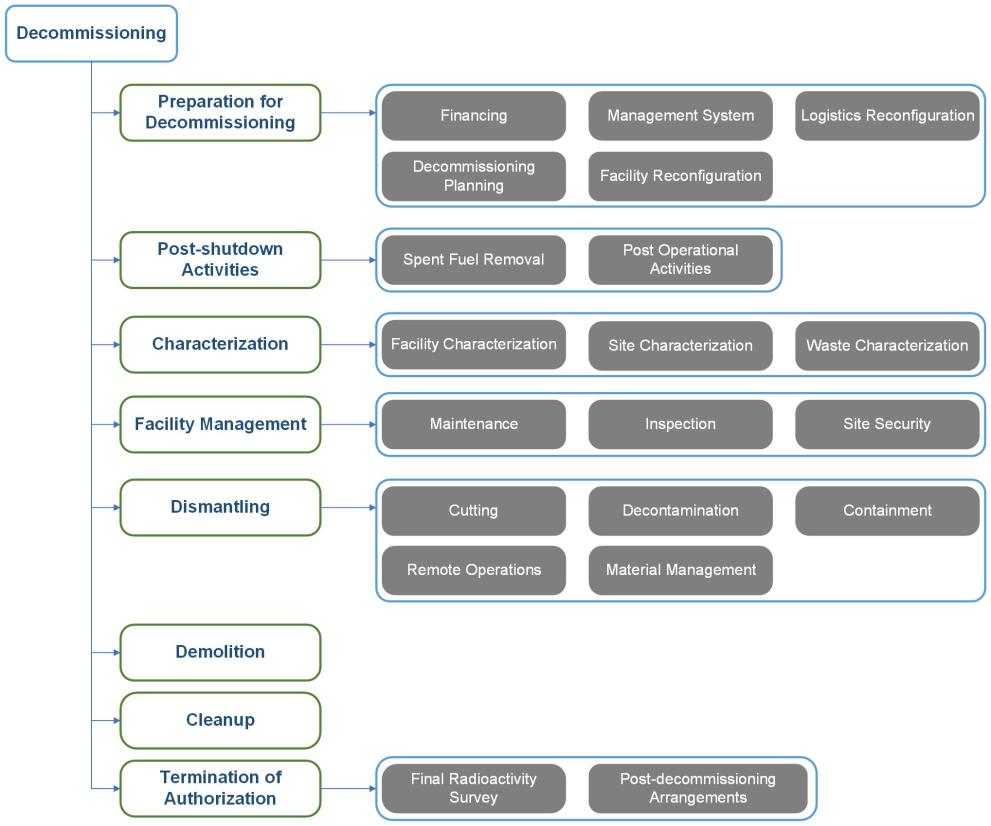
In 2021, the IAEA, the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) and the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre launched a collaborative exercise to facilitate the organization and interoperability of knowledge on the decommissioning of nuclear facilities, beginning with the creation of a common taxonomy for nuclear decommissioning.
Then IAEA published in 2023, A taxonomy for the decommissioning of nuclear facilities - TECDOC-2029, outcome of the collaborative work on the development of a nuclear decommissioning taxonomy. It was prepared jointly by the IAEA and the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre, in collaboration with the NEA.
The defined decommissioning taxonomies provide a hierarchical classification of things or concepts and it is applied to the following knowledge products (KP) produced in 2021-2023. In each is indicated the producer of the KPs, their content and the publication date.

This resource offers insights into selecting optimal decommissioning strategies and setting up initial projects, covering planning, costing, and licensing aspects. The expected increase in decommissioning activity will provide valuable guidance for stakeholders. It emphasizes the importance of Preliminary Conceptual Decommissioning Plans (FCDP) and aims to assist in selecting feasible alternatives, aid stakeholders, and inform key documents like Environmental Impact Assessments and National Program updates.
Financing
Activities required to ensure adequate financial resources are available when necessary for safe decommissioning.

JAVYS shares insights on implementing IAEA/NEA methodologies and Monte Carlo simulations for decommissioning risk management and cost estimates in V1 NPP's Decommissioning Project. Tailored for similar organisations, it provides practical examples, site-specific data, and basic MC simulation understanding. Offering use cases, it emphasises real-world applications, lessons learned, and practical recommendations.

This report guides nuclear decommissioning projects, presenting new cost estimation methods. It covers cost assessment, funding, and monitoring, emphasising accurate liability estimation for improved measurements and reduced risks. Precise funding and cost monitoring can mitigate delays and overruns, enhancing project quality and safety.
Decommissioning planning
In accordance with regulatory requirements, the preparation and maintenance (throughout the facility lifetime) of a plan to show how decommissioning can safely achieve the defined end state.

This resource offers insights into selecting optimal decommissioning strategies and setting up initial projects, covering planning, costing, and licensing aspects. The expected increase in decommissioning activity will provide valuable guidance for stakeholders. It emphasizes the importance of Preliminary Conceptual Decommissioning Plans (FCDP) and aims to assist in selecting feasible alternatives, aid stakeholders, and inform key documents like Environmental Impact Assessments and National Program updates.

This technical visit highlights SERAW's expertise in utilising 3D models for decommissioning and raw waste management. Aimed at decommissioning operators, it assists in determining the cost-effective approach and scope for 3D work. Participants gain insight into SERAW's tools and field experience, enhancing their understanding and proficiency.

Discover the 3DIMS (3D Information Management System) software's capabilities, introduced to JRC in March 2019, through this Knowledge Product. It offers practical guidance, contextual insights, and application examples in nuclear decommissioning engineering. Learn potential improvements and effective tips, and see screenshots for clarity. Equip yourself with actionable knowledge, promote its use beyond JRC, and benefit from enhanced collaboration and quicker data access.

The seminar comprehensively examines decommissioning programs, covering definitions, objectives, strategies, and radioactive waste management. It delves into programming, licensing, funding, cost estimation, and risk analysis, featuring an Italian case study and insights on decommissioning value and status. Additionally, it explores innovation in D&D and RWM, including internal projects and international cooperation.
Characterisation
Determination of the physical, chemical and radiological nature of something for the purpose of informing activities and decisions.

The "Guidance for developing an in-house methodology for radiological characterisation of conventionally non-radioactive waste" aids D&WM organisations in creating and applying internal materials and equipment free-release methodologies. Drawing from Ignalina NPP's experience, it offers recommendations for minimising effort and expenses in decommissioning, allowing for increased free release, income generation, and reduced RAW repository capacity.

The guideline "Establishment and Update of a Decommissioning Database in V1 NPP Decommissioning Process" underscores the importance of physical and radiological characterisation in the decommissioning phases. It provides technical guidance for compiling a comprehensive database, facilitating efficient planning, risk assessment, and cost estimation. Developed by JAVYS experts, it offers insights and tips for database creation and continuous updating, aiding nuclear facility decommissioning efforts while ensuring regulatory compliance and safety.

This Knowledge Product offers guidance in managing decommissioning and contaminated soil. The report outlines methodologies for digital data management, geodatabase creation, interpolation procedures, and 3D modelling, aiding in optimal process management. It aims to assist in developing a methodological approach to environmental activities, providing technical guidance through 3D modelling software. The guidelines facilitate learning and acquiring a methodological approach, enhancing safety and cost-effectiveness in managing potentially contaminated soil and water during decommissioning.
Waste characterisation
Determination of the physical, mechanical, chemical, radiological and biological properties of radioactive waste to establish the need for further adjustment, treatment or conditioning, or its suitability for further handling, processing, storage or disposal.

This lessons-learned report compiled by experts from JRC at JRC-Ispra, Italy, reflects the FARO dismantling. It offers guidance on nuclear decommissioning and proposes new methodologies and lessons from FARO. The report identifies hurdles in clearance processes and offers insights into planning, material identification, and instrumentation.

The FARO dismantling project at JRC-Ispra marks a significant decommissioning effort. Split into two phases, it aimed to assess progress and inform future projects, notably the INE deconstruction. This knowledge product draws from FARO's experience, guiding preliminary activities for clearance procedures in decommissioning projects. It incorporates lessons learned, contamination reports, and software data to optimise costs, time, and safety.

The "Guidance for developing an in-house methodology for radiological characterisation of conventionally non-radioactive waste" aids D&WM organisations in creating and applying internal materials and equipment free-release methodologies. Drawing from Ignalina NPP's experience, it offers recommendations for minimising effort and expenses in decommissioning, allowing for increased free release, income generation, and reduced RAW repository capacity.
Dismantling
The taking apart, disassembling and tearing down of the structures, systems and components of a facility (within a radiologically controlled area) for the purposes of decommissioning.

Modifying liquid radioactive waste treatment technology at INPP involves bituminisation and cementation units. Bituminisation since 1987 and cementation since 2006. The shutdown of power units increased Cs137 activity in concentrate, necessitating optimised solidification. Challenges include leaching, volume increase, and physical property limitations. Research led to optimised recipes and improved packaging for safer storage.

The Workshop fosters dialogue among participants, facilitating knowledge exchange on INPP's Radioactive Metal Waste Treatment Facility installation. Targeted at EU decommissioning operators and stakeholders, it shares insights on design, construction, and operation. Attendees gain insights into selection processes, investments, and operational tools used by INPP, leveraging their field experience.

This document compiles SERAW's experience in constructing and operating a Plasma Melting Facility for treating RAW at Kozloduy, emphasising improvements and lessons learned compared to traditional treatment methods like Super Compactation. It aims to transfer practical experiences, focusing on efficiency and cost performance, to organisations interested in adopting similar technologies.

This guideline outlines the process, requirements, and responsibilities for freeing materials from radiological control, focusing on fixed geometries like drums or pallets. Drawing from SERAW's experience during the decommissioning of Kozloduy NPP Units 1 to 4, it offers practical insights to prevent radioactive material spread and reduce decontamination costs. Aimed at organisations conducting measurements and assessments for free release, it assists in developing processes compliant with national and international regulations (IAEA Safety Series No. 89). While not a formal, high-level guidance, it provides specific tips and recommendations for European operators.
Decontamination
The complete or partial removal of contamination by a deliberate physical, chemical or biological process.

The Seminar on "Development of the Strategy of Large Components Fragmentation of V1 NPP Primary Circuits" presents insights from JAVYS experts at V1 Nuclear Power Plant, Slovakia. Project D4.2's experience highlights the importance of a well-defined fragmentation strategy for primary circuit components. Offering tips and lessons learned, it addresses key questions and demonstrates strategy flexibility for successful implementation.

This case study provides comprehensive guidance for decommissioning and waste management organisations, covering project phases from preparation to achieving objectives. Developed by JAVYS experts, it shares insights from the BIDSF Projects D2 and D2-A, sponsored by the European Commission and Slovak nuclear fund. The study assists in planning and implementing primary circuit decontamination projects, offering valuable insights and lessons learned.
Material management
The setting up of routes for and subsequent removal of structures, systems, components and material in the facility.

This document presents the experience and lessons learned by Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant (INPP) in the analysis and application of Liquid Radioactive Waste (LRW) technologies during the decommissioning program of INPP Unit 1 and 2 and auxiliary facilities.
The overall goal is to convey relevant knowledge to other European Union (EU) decommissioning operators to support their own LRW activities, with a focus on:
▪ The selection of technology for LRW treatment.
▪ The preparatory works for the installation of LRW treatment facilities.
▪ The operation of LWR facilities

The Workshop fosters dialogue among participants, facilitating knowledge exchange on INPP's Radioactive Metal Waste Treatment Facility installation. Targeted at EU decommissioning operators and stakeholders, it shares insights on design, construction, and operation. Attendees gain insights into selection processes, investments, and operational tools used by INPP, leveraging their field experience.

This document aims at compiling the experience acquired by SERAW in the construction and operation of a Plasma Melting Facility used to treat RAW at Kozloduy, with a focus on improvement and lessons learned concerning traditional treatment technologies such as Super Compactation. The goal is to facilitate the transfer of practical experiences, fusing on throughout and cost performance of SERAW to organizations willing to develop and use similar technologies.
Waste management
Although the "waste management" concept is not included in the Taxonomy of Nuclear Decommissioning Activities as a "core concept", it is included as an "enabling concept" to link with the knowledge field of radioactive waste management. The knowledge products conveyed in this section are tagged with the "waste management" label since they are strongly related with different radioactive waste management activities.
Waste management: all administrative and operational activities involved in the handling, pretreatment, treatment, conditioning, transport, storage and disposal of radioactive waste [IAEA/NSS/GLO, IAEAL 22-01539 | ISBN 978–92–0–141122–8].
Soil and groundwater environmental data management and modelling for decommissioning of a nuclear site

LESSONS LEARNED IN FARO DISMANTLING PROCESS I

