Our mandate and activities (as outlined in Directive 2010/63/EC on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes) cover the entire life cycle of alternative methods, i.e. from development over validation to regulatory acceptance, international recognition and proper scientific use.
At the core of these activities is the EURL ECVAM validation process.
Validation is at the interface between test method development/optimisation and regulatory acceptance/international recognition and ensures a science-based and rigorous evaluation of test methods (Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment (IATA) or Defined Approaches (DA)), independent of special interests, establishing their overall performance and fitness for a given purpose, i.e. their scientific validity.
In principle, test methods and approaches could also be validated by other actors than validation bodies such as e.g. test method developers in academia and industry and then reviewed within other neutral (with respect to the test method) processes, such as e.g. the OECD review process within the OECD Test Guidelines Programme.
The EURL ECVAM validation process allows for a consistent execution of all EURL ECVAM validation studies and encompasses four key steps (Figure 1).
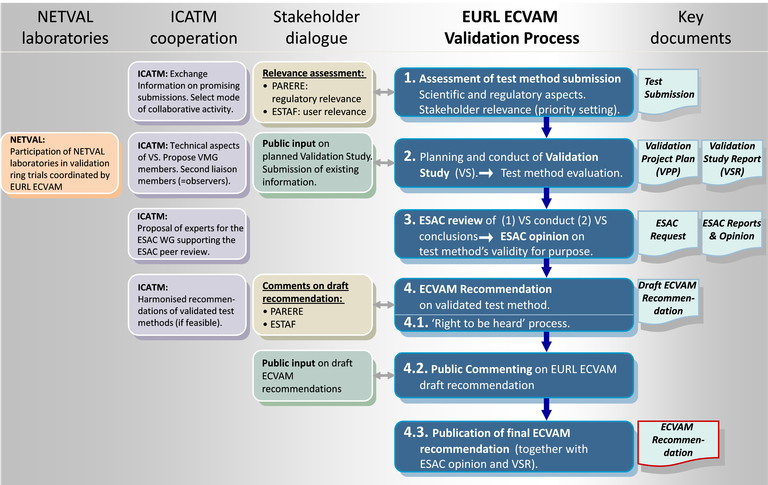
The process (blue) encompasses four key steps. Interactions with stakeholders (EURL ECVAM's Network for Preliminary Assessment of Regulatory Relevance (PARERE) and EURL ECVAM Stakeholder Forum (ESTAF)), International Collaboration on Alternative Methods (ICATM) and European Union Network of Validation Laboratories (EU-NETVAL) are indicated to the left of the process. Key output documents on the right.
The process steps are:
1. Assessment of test method submissions taking stakeholder and ICATM input into account;
2. Planning and conduct of validation studies, possibly in collaboration with EU-NETVAL laboratories;
3. Coordination of independent scientific peer review by the EURL ECVAM Scientific Advisory Committee (ESAC)
4. Development of EURL ECVAM Recommendations on the validity status of test methods taking stakeholder and ICATM input into account.
Step four is further subdivided: 4.1 test method submitters have the possibility to comment on draft EURL ECVAM Recommendations prior to their publication ("Right-to-be-heard process") 4.2 invitation of comments from the general public; 4.3 Finalisation of EURL ECVAM Recommendation, taking into account the comments received. Finally, publication of the EURL ECVAM Recommendations on the website of EURL ECVAM.
During the process, stakeholders, international partners and also test method submitters are involved at key stages, so that their views but also their technical and scientific input is taken into account to the extent possible.
Step 1 - Assessment of proposed (submitted) test methods and priority setting
- Scientific assessment of test method proposals submitted to EURL ECVAM.
- Solicitation of input from EURL ECVAM's consultation bodies, PARERE and ESTAF, concerning the regulatory and stakeholder relevance of submitted test methods.
- Input, if required, from ESAC on specific test method proposals, e.g. in view of establishing whether proposed putative similar test methods (also called 'me-too methods') are indeed sufficiently similar to already validated ones so that they can be validated through Performance Standards-based validation.
- Interaction with validation bodies of other countries/areas in the framework of ICATM. The aim is to orchestrate validation efforts and exchange views and information on the various regulatory requirements.
- Prioritisation of individual test methods or integrated approaches considering in particular EU regulatory requirements and urgencies.
- Prioritised test methods may be included in a validation study coordinated by EURL ECVAM (step 2).
Step 2 - Planning and execution of validation studies
- Public input (e.g. via a call for data and protocols) on planned validation studies to ensure that all relevant existing information is being taken into account prior to validation design and execution.
- Design and set-up of validation studies including ex-ante definition of objectives of the study and purpose of the test method (e.g. specific use in an ITS or the regulatory context)
- Scientific, technical and regulatory input from ICATM partners on planned validation studies.
- Set up of international Validation Management Teams in agreement with EURL ECVAM validation principles and those outlined in OECD Guidance Document No. 34 concerning validation of alternative methods.
- Coordination of validation studies (i.e. multi-laboratory trials) involving, where possible, laboratories of the EU-NETVAL run by EURL ECVAM.
Step 3 - Coordination of the scientific peer review of validation studies coordinated or evaluated by EURL ECVAM
- Completed validation studies undergo independent scientific peer review by ESAC.
- Specialised Working Groups (WGs) of ESAC are set up ad hoc to prepare ESAC peer reviews and document their findings in "ESAC WG Reports". WGs are typically composed of ESAC members and external scientists (nominated by ESAC, EURL ECVAM and ICATM partners).
- EURL ECVAM coordinates the work of ESAC WGs and the ESAC peer review process, ensuring a consistent approach to all reviews conducted.
- The output of ESAC consists in "ESAC Opinions" which summarise the scientific advice given to EURL ECVAM.
Step 4 - Development of EURL ECVAM Recommendations on the validity status of test methods
- Drafting of EURL ECVAM Recommendations summarising the validity status of test methods, their mechanistic relevance, performance, limitations and applicability, taking into account the ESAC Opinion, EURL ECVAM's own evaluation and other relevant information.
- Input on draft Recommendations from stakeholders (PARERE, ESTAF) and ICATM partners ("restricted commenting").
- Comments from the test method submitter ("right to be heard" process) on the draft Recommendation.
- Invitation of comments on draft Recommendations from the general public (draft Recommendations are published on EURL ECVAM's website at this stage). Finalisation of EURL ECVAM Recommendations balancing, in an impartial manner, EURL ECVAM's own position with all other input received (ESAC, stakeholders, test method submitters, general public, international partners).
- Publication of the final EURL ECVAM Recommendation following endorsement by the JRC Directorate F - Health, Consumers and Reference Materials hosting EURL ECVAM.
