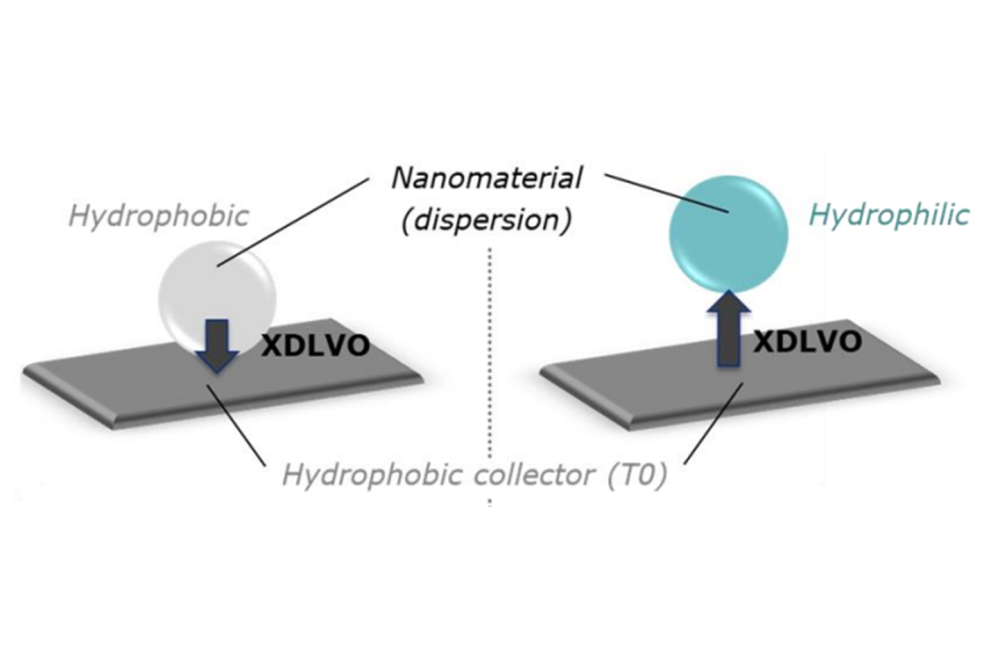
This technology offers a quantitative, robust, and easy-to-perform solution, filling a gap in the market as there are no current methods to measure nanomaterials' (NMs) hydrophobicity at scale.
Details
Patent: WO2016177641
Publication date: 10 November 2016
Fields of use
This technology can be applied in industries involving nanomaterial production, especially within nanomedicine, where hydrophobicity significantly impacts functionalities like protein adsorption, biological membrane interactions, and cellular uptake. It also applies to environmental compliance, as hydrophobicity influences the fate and bioaccumulation of NMs, with regulatory bodies like REACH already setting the stage for mandatory characterization.
Main advantages
- Fast and efficient: Takes only a few minutes with minimal sample volume required for testing.
- Ease of use: Samples are simple to prepare and the method can be fully automated.
- OECD recognition: Adopted as a reference OECD Guideline in 2023, proving its robustness and reliability.
- Proven and tested: Successfully assessed in real-world environments and validated through an inter-laboratory comparison across 9 labs in 8 countries.
- Commercially viable: Offers a strong potential for integration into production lines, especially for the pharmaceutical industry, with options for both consumable sales and complete screening devices.
Competitive edge
Compared to other hydrophobicity measurement methods, this technology stands out with its speed, efficiency, automation compatibility, and the comprehensive nature of the data it provides.
| Criteria | Octan/water | Dye absorption | Contact angle | Chromatography | Affinity to collectors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For nanomaterials | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Range (nm) | 1 to 2000 | 1 to 2000 | 1 to 2000 | 1 to 2000 | 10 to 2000 |
| Quantitative | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Min. sample qty | Few mg | 10s of mg | 100s of mg | 10s of mg | few mg |
| Additional sample preparation | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Reproductibility | Good | Good | Poor | Good | Good |
| Assay duration (h) | 1 | 24 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Hardware cost (k€) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 to 100 | 25 |
| Comsumable costs (€) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 5 |
| Business potential | Low | Medium | Low | Low | High |
| Real-time use on production lines | No | No | No | No | Yes |
Comparison of the JRC developed technology with other methods to determine NMs hydrophobicity.
