
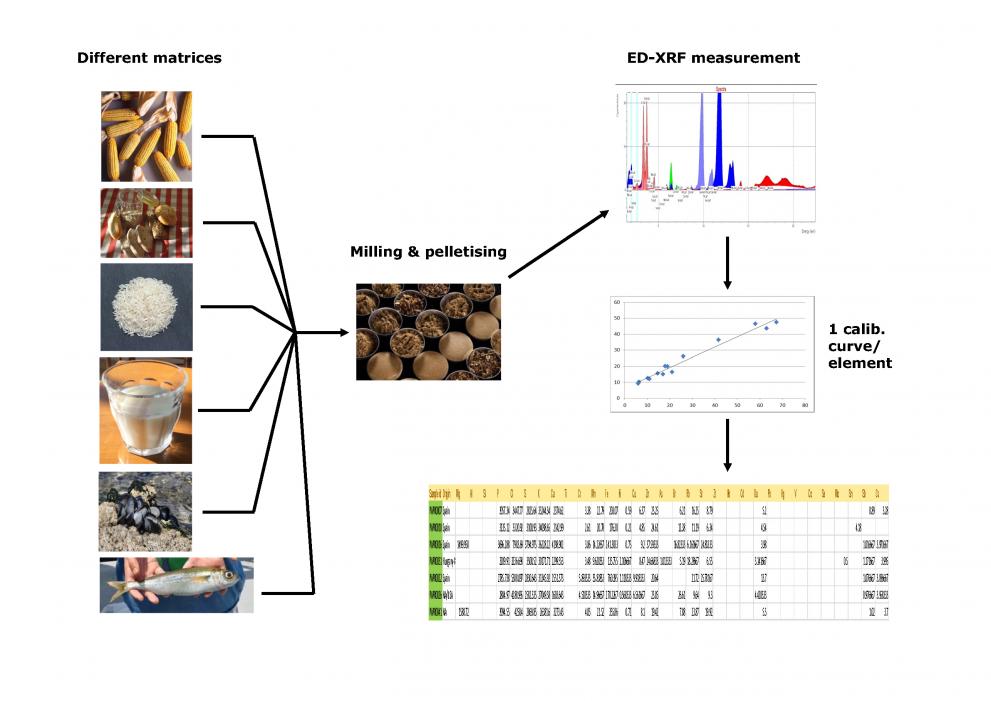
With the aim to support routine control laboratories, JRC scientists developed a new approach to validate an analytical method for the determination of trace elements which hardly requires any sample pre-treatment. The method is applicable for the determination of heavy metals in sediments, soils, cereals, tobacco, feed, fish and milk.
Routine public and private analytical laboratories need methods of analysis that can be used with very different purposes such as
- fraud detection
- health
- control of environmental pollution
- identification of illicit substances
- security
The development and validation (required when laboratories are accredited) of specific methods for each of the substances to be analysed is expensive and time consuming and hence not fit for the needs of the modern control laboratories.
Determination of trace elements which is of paramount importance in areas such as nutrition, clinical tests, toxicology, environmental protection and fraud prevention, has been traditionally done with methods of analysis that require a cumbersome and complex sample digestion with harsh chemical reagents.
In recent years, alternatives to those tedious methods have been developed, energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (ED-XRF) being one of them.
Milling of solid samples and formation of pellets under pressure with the obtained powder is all the sample pre-treatment needed to measure trace elements with ED-XRF. However, ED-XRF has one major drawback which is the need to construct calibration curves for each of the elements that can be measured in one single run (from sodium to uranium), for the different matrices to be analysed.
Therefore, JRC scientists developed a new validation strategy for an ED-XRF method to determine a number of trace elements in a wide range of organic and inorganic matrices.
The approach was based on fulfilment of method performance criteria and can be easily implemented by laboratories without much experience in the use of ED-XRF.
Once the validation has been finalised in a specific laboratory, the method can be applied to determine many different elements, in many different types of samples (mineral and organic), and in a wide range of concentrations.
Control laboratories in multiple domains are expected to benefit of the approach proposed by the JRC.
- Read more in: Y. Fiamegos and M.B. De la Calle: "Validation strategy for an ED-XRF method to determine trace elements in a wide range of organic and inorganic matrices based on fulfilment of performance criteria", Spectrochimica Acta Part B 150 (2018) 59-66
Related Content
Details
- Publication date
- 5 March 2019
