Artificial intelligence (AI)
Evolution in the international landscape
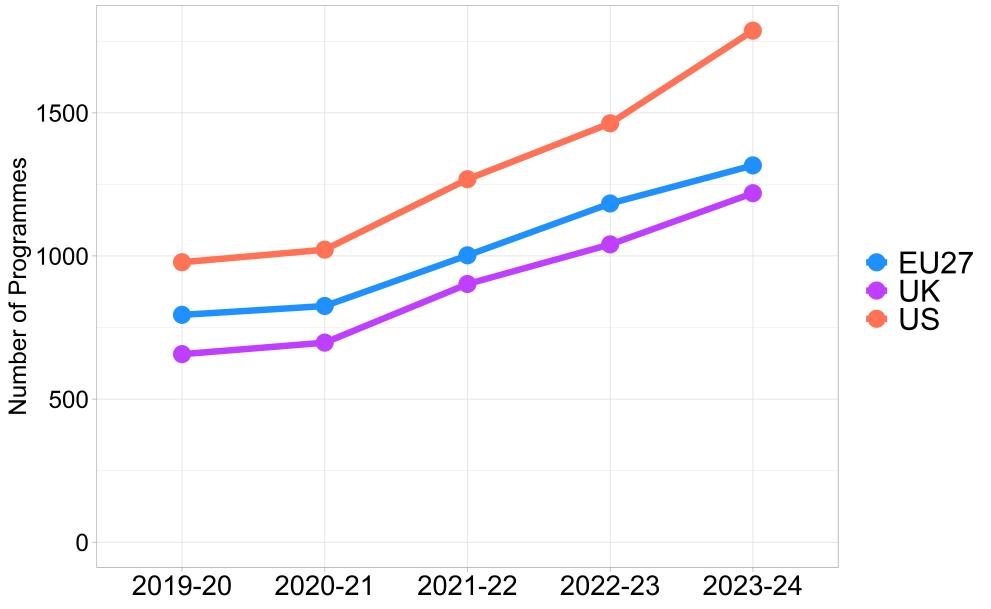
- In the academic year 2023-24, the offer of Artificial intelligence master’s programmes is led by the US (with 1,787 master’s programmes), with the EU showing improvement over time but lagging behind in all considered years (1,316 in the last academic year, growing from 794 in 2019-20).
- The evolution of specialised master’s offer in the EU, the US and the UK is very similar and positive showing an increase in the number of specialised master’s programmes in the academic year 2023-24.
- In specialised master's programmes —those focused on the technological domain— the EU leads (567), slightly above the US (561) and the UK (521).
- In the EU, 9.42% of master’s in 2023-24 have an AI component, a share that is quite above that in the US (4.33%) and the UK (6.03%).
Content areas
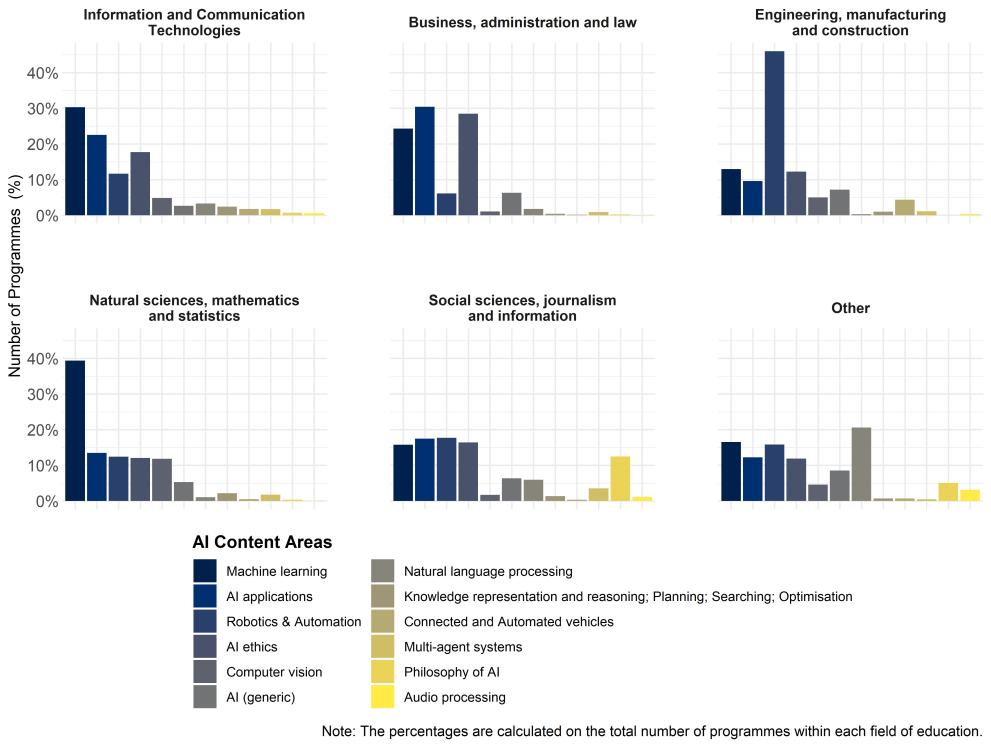
- In the main considered geographical areas (EU, UK, US) 'Machine learning' is the most frequent content taught.
- 'AI applications' is in the second position overtaking 'Robotics & Automation' with respect to the previous academic year.
'AI ethics' remains stable in the fourth position as in 2022-23.
Fields of education
- 'ICT' is the main field of education in which AI content is taught, followed by 'Engineering' studies and 'Business, administration and law' studies. There are no remarkable changes with respect to 2022-23.

Content areas and Fields of education in the EU
- The content related to 'Robotics & automation' leads in the field of education 'Engineering, manufacturing and construction'.
- The field of education 'Business, administration and law' is mainly focused on 'AI applications' and 'Machine learning'.
High-performance computing (HPC)
Evolution in the international landscape
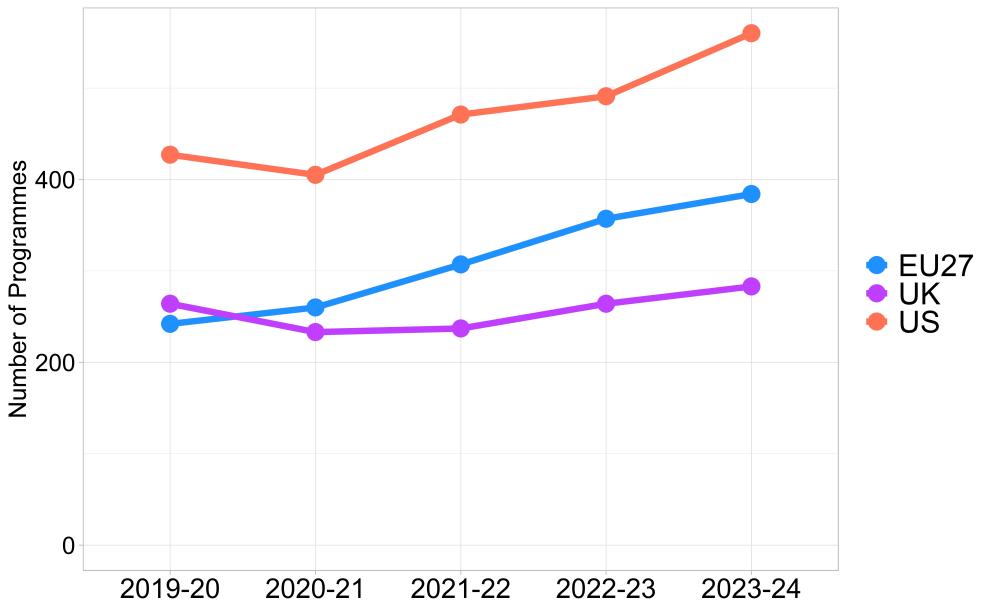
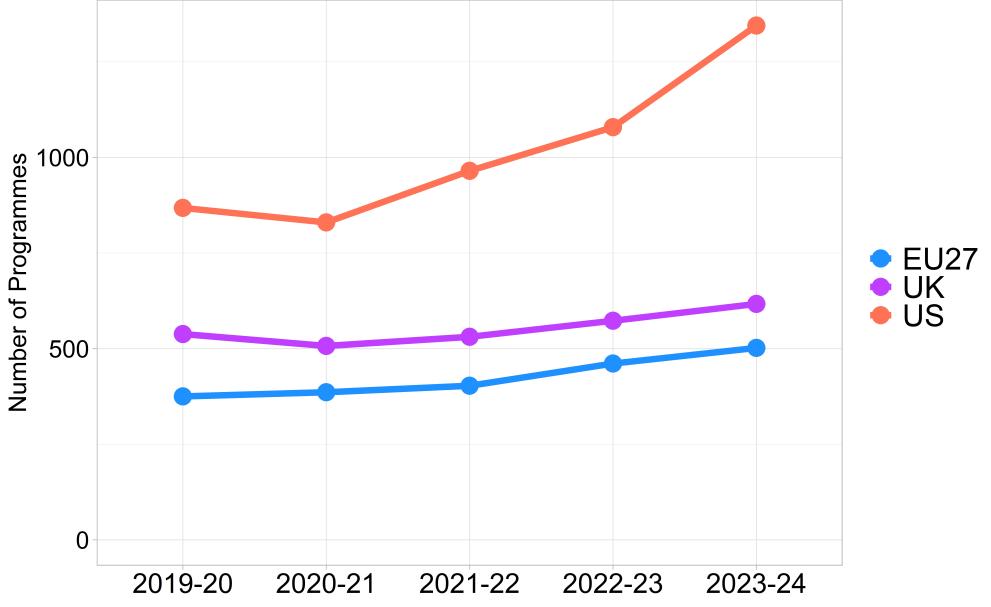
- The academic offer of High Performance Computing is again led by the US in 2023-24 (560), with the EU showing improvements and overtaking the UK since the academic year 2020-21 (384 and 283 programmes respectively in 2023-24).
- The offer of specialised HPC master’s programmes shows a consistent and significant increase since 2019-20, showing in the EU a cumulative increase of 189% in the last four academic years.
- The specialised master’s programmes offer in the EU (81 programmes) is higher than the one in the UK (56), but lower than in the US (101).
- The share of EU masters including high-performance computing content reaches 2.75% in the 2023-24 academic year, almost doubling that in the UK (1.40%) and in the US (1.35%).
Content areas
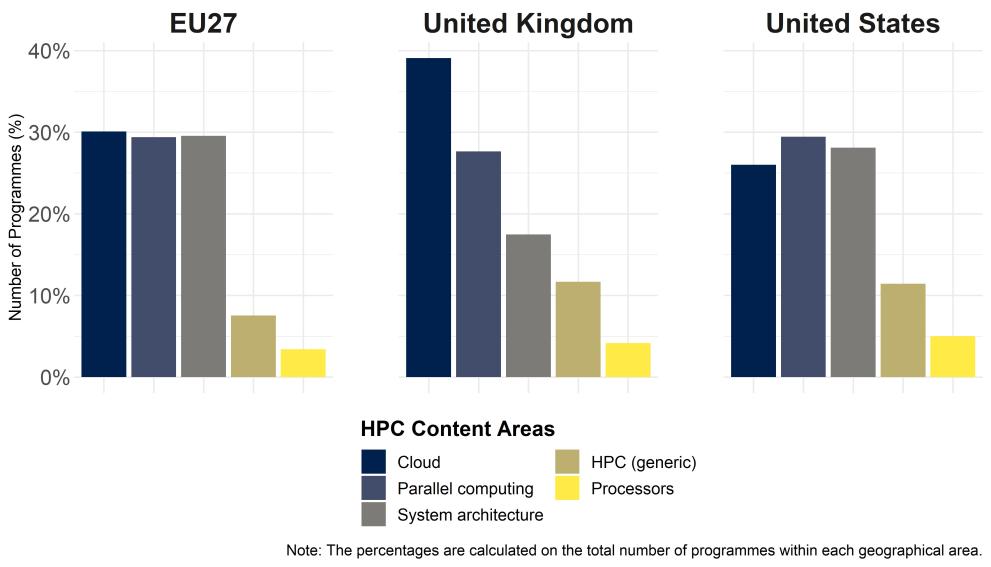
- The EU offer is almost equally focused in the content areas of 'Cloud', 'Parallel computing' and 'System architecture'.
- The US presents a distribution by content areas very similar to the one in the EU, with a lower share of 'Cloud' and a larger share of 'HPC (generic)'.
- The UK presents a remarkable focus in 'Cloud' content.
There are no remarkable changes with respect to 2022-23, except for a slight decrease of the 'Cloud' content in the EU.
Fields of education
- 'ICT' remains by far the main field of education in which HPC content is taught, followed by 'Engineering' studies (in broad master’s programmes) and by 'Business, administration and law' studies (in specialised master’s programmes), while other fields have very low prevalence.
Content Areas and Fields of education in the EU
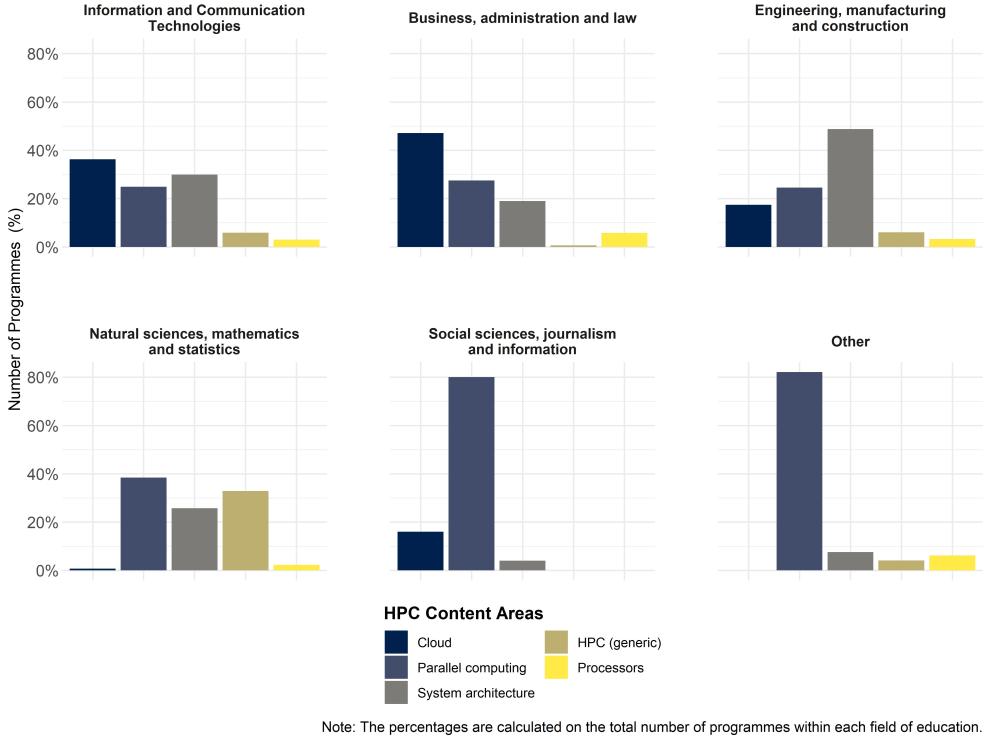
- In the EU, the field of education 'ICT' presents a balanced distribution of contents related to 'Parallel computing', 'Cloud' and 'System architecture'.
- The content area related to 'Cloud' is leading in the field of education 'Business, administration and law', but with a higher share compared to the previous academic year (2022-23).
- In the field of education 'Engineering, manufacturing and construction', there is a strong focus in the content areas of 'System architecture' and 'Parallel computing', with the latter presenting a much larger share than in the two previous academic years.
Cybersecurity (CS)
Evolution in the international landscape
- In the academic year 2023-24, the offer of Cybersecurity is led by the US (1,345 master’s programmes), followed by far by the UK (617), with the EU lagging behind (502). In addition, the offer of the US appears to have remarkably increased during the last academic years, which increases the gap with respect to the EU and the UK.
- Regarding specialised master’s programmes, the offer in the EU is quite stable over time, with a modest positive trend, but also lags behind both the US and the UK.
- In the EU, 3.59% of master’s programmes in 2023-24 have a cybersecurity component, slightly above the share in the US (3.26%) and the UK (3.05%).
Content areas
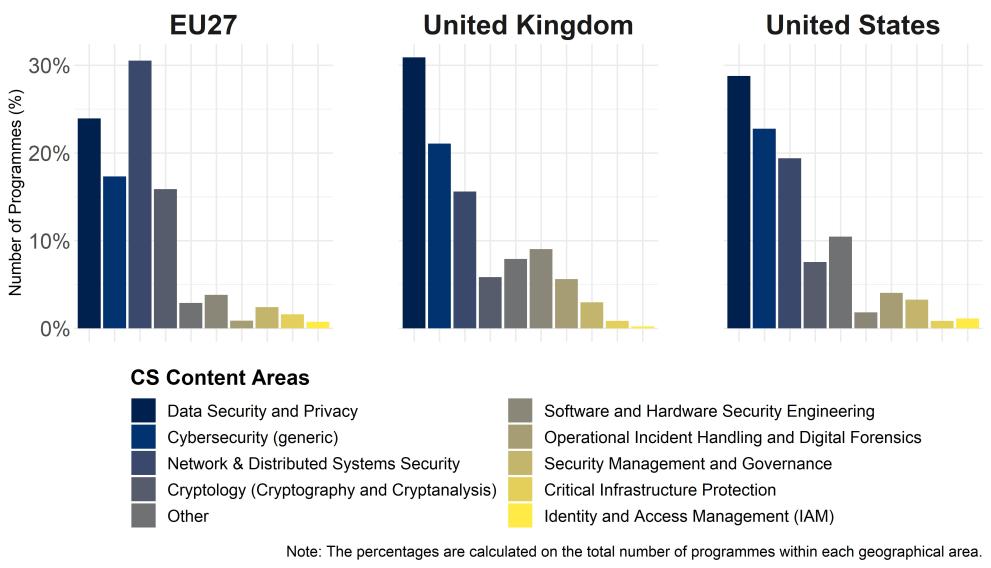
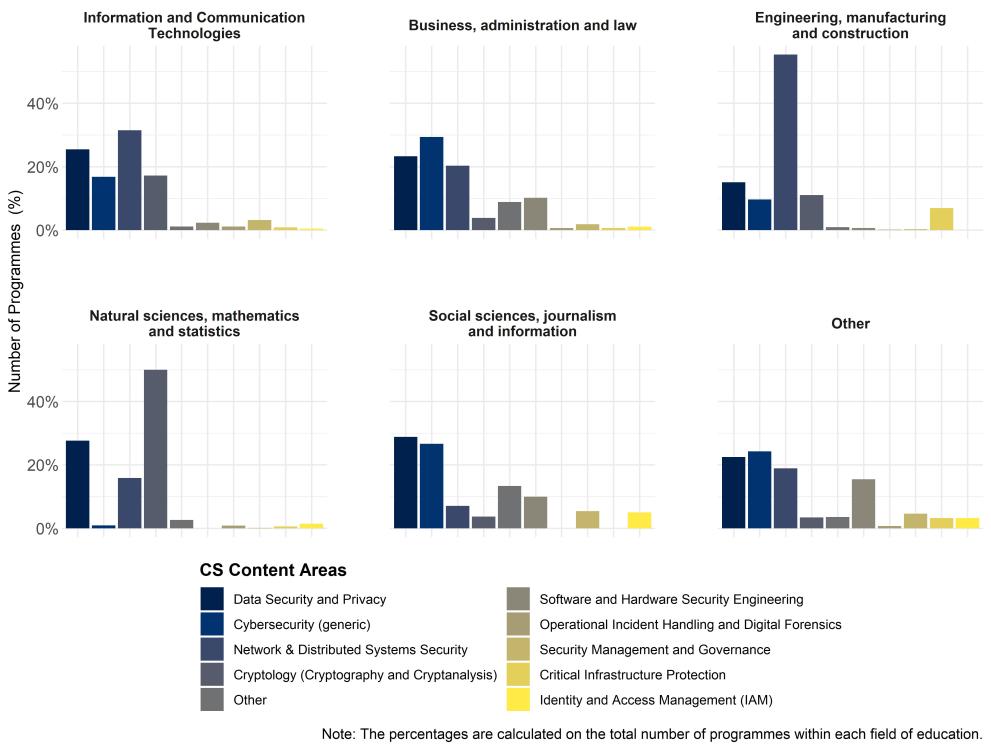
- In 2023-24, the principal area of content in EU master’s programmes is 'Network & Distributed Systems Security', while the US and the UK’s offers are mainly focused on 'Data Security and Privacy', with no changes with respect to 2022-23.
For the EU, the share of 'Cryptology (Cryptography and Cryptanalysis)' is relatively high (around 15%) when compared to that in the US (8%) and the UK (5%), but decreasing with respect to last year.
Fields of education
- 'ICT' is undoubtedly the main field of education in which CS content is taught.
- Regarding specialised master’s programmes, the offer is even more concentrated in the ICT field (70% of programmes are taught in ICT studies).
Content areas and Fields of education in the EU27
- In the EU, the field of education “ICT” is mainly focused in the content area of “Network & Distributed Systems Security”, with a respectable share related to “Data Security and Privacy” as well.
- “Cybersecurity (generic)” is the main content taught in the “Business, administration and law” field of education.
- In the EU, the field of education “Engineering, manufacturing and construction” is very focused on the content area regarding “Network & Distributed Systems Security”.
Data science (DS)
Evolution in the international landscape
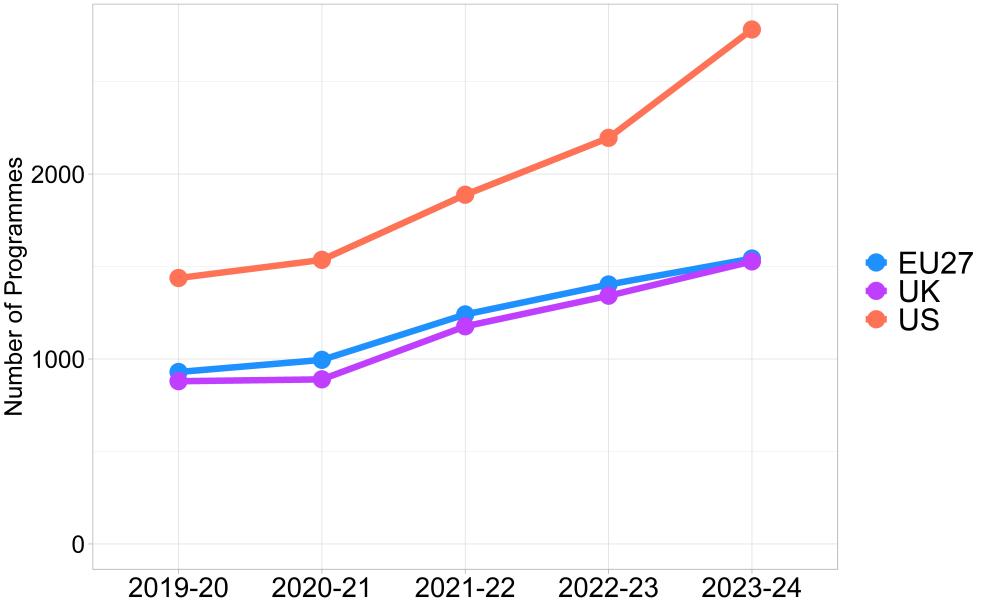
- In 2023-24, the offer of Data Science master’s programmes is led by the US (2,782 programmes), which presents a considerable increase over time, almost doubling the offer since 2019-20. EU’s offer mirrors that in the UK in all years analysed.
- The specialised master’s offer in the EU and the UK are also very close and present similar trends, with increases of 10% and 15% respectively in the last academic year. US’s offer is larger in any considered year and growing faster (31% in the last year).
- The trends show that the US increases its gap with respect to the EU and the UK significantly this academic year.
- In the 2023-24 academic year, the proportion of EU masters teaching data science is 11.04%, far from the 6.74% in the US and 7.56% in the UK.
Content areas
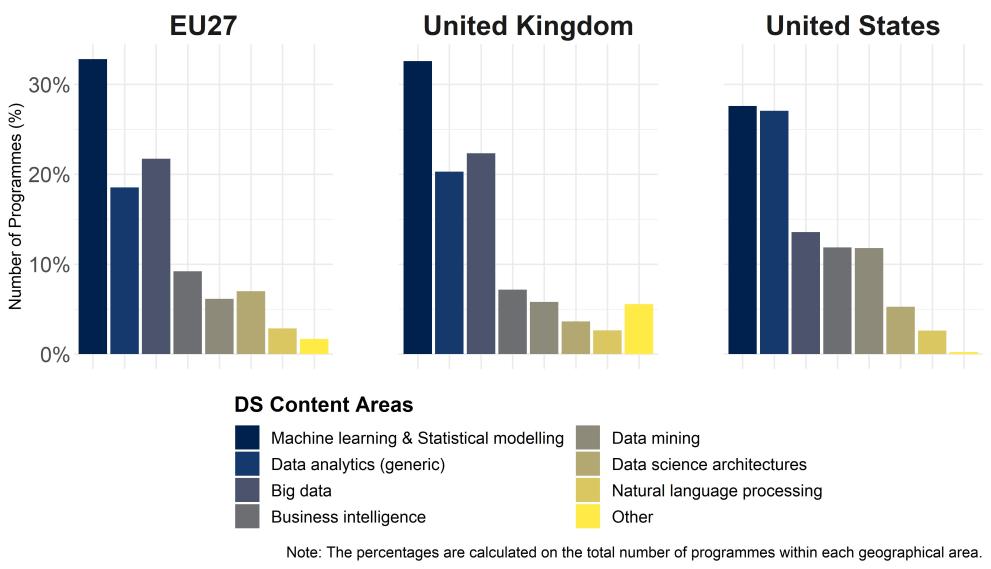
- 'Machine learning & Statistical modelling' appears as the main content area taught in DS.
- Compared to last year, in the US the share of 'Data analytics (generic)' has slightly increased.
The content area 'Big Data' has a modest share in the US (around 15%), while in the UK and the EU it is much larger (around 25% and 22%, respectively).
Fields of education
- 'ICT' is undoubtedly the main field of education concerning DS specialised master’s.
- DS broad master’s programmes are primarily taught in the field of education of 'Business, administration and law', closely followed by 'ICT'.
- The US presents a remarkable offer of DS specialised master’s programmes in the field of education 'Business, administration and law'.
Content areas and Fields of education in the EU
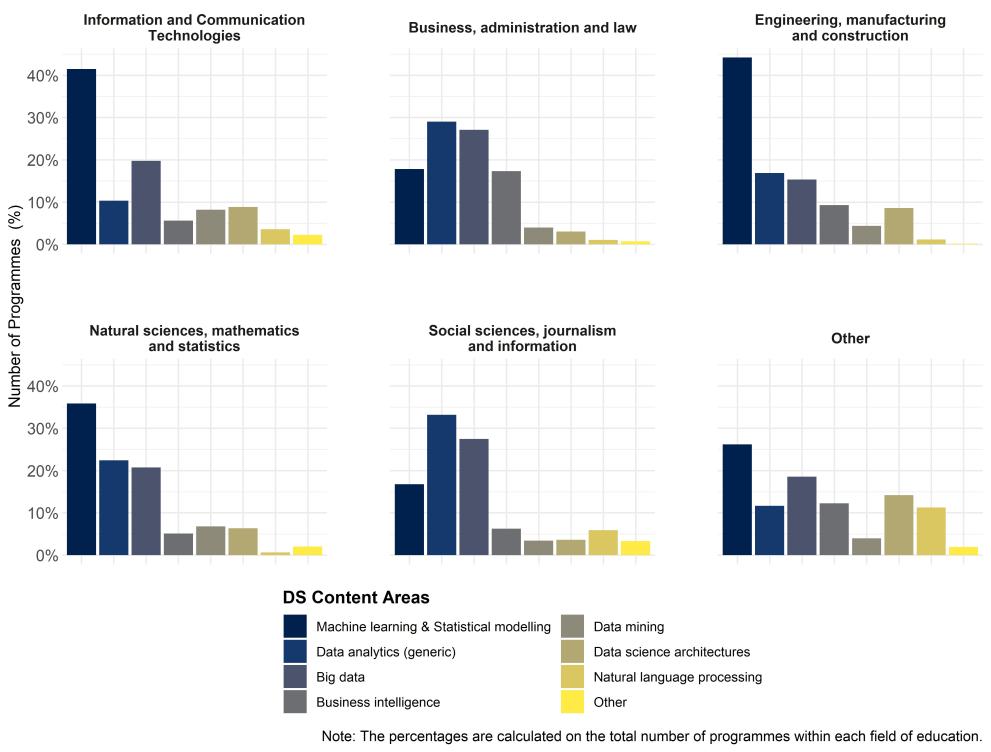
- In the EU, the content area 'Machine learning & statistical modelling' holds the largest share (around 45%) in the fields of education 'ICT' and 'Engineering, manufacturing and construction'.
- The field of education 'Business, administration and law' presents a main focus in four content areas, with the one concerning 'Big data' in the first position, closely followed by 'Data analytics (generic)'.
- The education field 'Engineering, manufacturing and construction' is very concentrated in 'Machine learning & statistical modelling'.
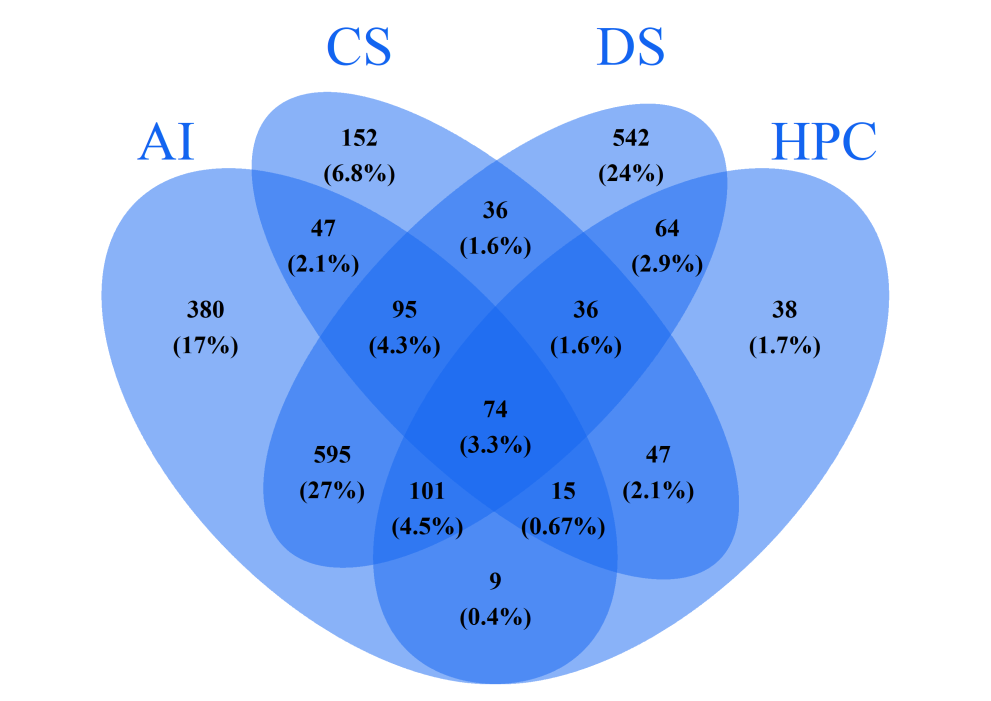
Overlaps in the offer of digital domains
- Considering the four domains jointly (AI, HPC, CS, DS), the US clearly leads the master’s offer, with 4,146 programmes in at least one of the four domains. The EU lags behind, with 2,231 programmes, very similar to the UK (2,306).
- In the EU, in 2023-24 artificial intelligence and data science present a considerable intersection in terms of education offer (similar to what seen in 2022-23). Out of the education offer in the four domains jointly considered, 39% of the EU programmes fall simultaneously under the domains of AI and DS.