Advanced manufacturing is defined as the use of innovative technologies to what and how we produce. It involves the integration and convergence of technologies like automation, robotics, artificial intelligence and digitally connected solutions, to enable the emergence of new industrial products, processes and business models.
The JRC study “Advanced Manufacturing Study. Preliminary findings on EU's Advanced Manufacturing industry in the global landscape” sheds light on the state of the play of European advanced manufacturing (ADMAN) activities powered by digital technologies, its strength and innovative capacity. By doing so, it provides a comprehensive and comparative global overview of the advanced manufacturing industry.
The ADMAN industry is a key enabler for European competitiveness. It is considered critical for the EU’s economic security and industrial resilience, and crucial for the manufacturing of net-zero technology for the green transition.
A remarkable rising of European firms engaged in advanced manufacturing
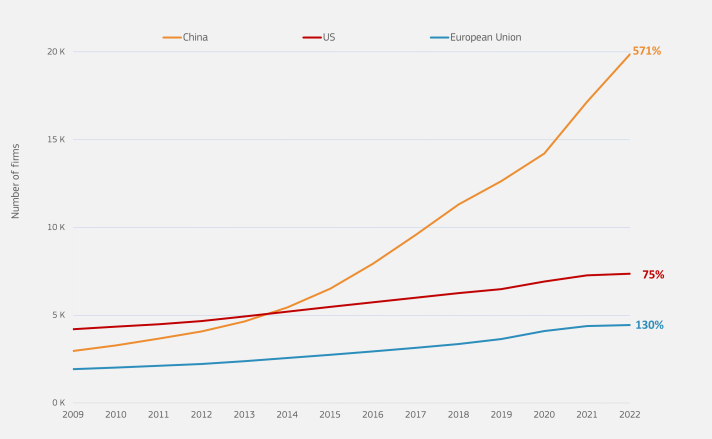
The report resulting from the study shows a significant increase in the number of firms engaged in advanced manufacturing in the EU, with a concentration in Germany, Spain, France, and Italy.
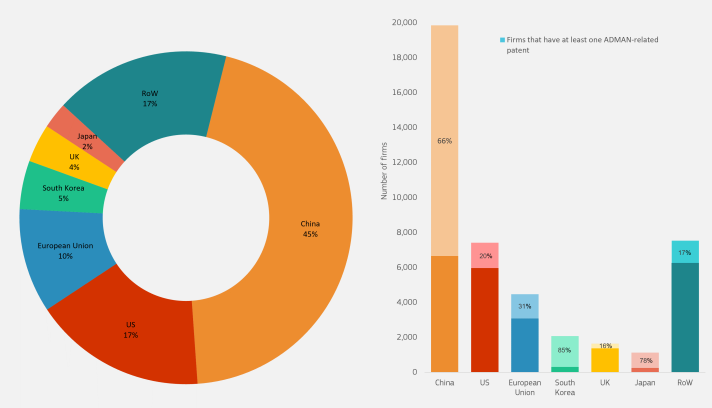
According to the data, the number of firms engaging in advanced manufacturing in the EU rose remarkably in the period 2009-2023, passing from 1,900 to 4,500, which represents slightly more than 10% of advanced manufacturing firms worldwide. These firms have as core businesses and/or patents related to the industrial application of advanced technologies to manufacturing processes.
When looking worldwide, we observe that the landscape is highly concentrated, as 72% of ADMAN firms are located in China, the US or the EU. Zooming in to the EU, we can observe further that the advanced manufacturing landscape is concentrated in a few countries, with Germany, Spain, France, and Italy together hosting almost 60% of all EU firms engaging in advanced manufacturing activities.
Distribution of advanced manufacturing activities: 3D printing is the largest technology area
By looking at the technological distribution of activities, it is interesting to notice that it is rather homogeneous across the European Member States, with EU firms focused on Artificial Intelligence, 3D Printing, Dynamic Data, and Robotics.
3D Printing is the largest advanced manufacturing technology area within the ADMAN industry, accounting for 39% of activities using this technology in Europe, as well as the main tech area in China and US.
China maintains a leading position in the advanced manufacturing industry
The EU has been growing faster than the US in recent years, but China has a leading position in terms of the number of advanced manufacturing firms and innovation. By looking at the chart below, we can observe at first glance the sharp increase of Chinese firms in the ADMAN landscape.
China, the EU and the US display a rather similar technological composition of advanced manufacturing activities, but with some relevant differences. In particular, the study shows that China has a larger percentage of ADMAN-related activities in the technology area of semiconductor and power electronics (23%) compared to the EU (13%) and the US (13%).
Foreign ownership of European firms is dominated by US investors
Besides the technology distribution of activities, the study presents findings on the ownership structure of European advanced manufacturing firms, as well as venture capital investments.
The data shows that 18% of European firms engaging in ADMAN-related activities are foreign owned. Despite US companies control one out of three foreign-owned ADMAN firms in the EU, the EU leads in controlling foreign-owned ADMAN firms worldwide, as the ultimate owner of 34% of foreign-owned ADMAN firms is located in a European country.
On venture capital, it is noteworthy that EU firms have significantly worse access to Venture Capital (VC) compared to the US and China. Out of global Venture Capital investments, only 5% went to EU firms.
Next steps – Diving into advanced manufacturing across industrial ecosystems
These preliminary findings are part of a broader study on the Advanced Manufacturing industry. They offer a first insight into the relative position of the EU with respect to its main global competitors, and an overview of the advanced manufacturing industry in Europe and globally.
In the coming weeks, JRC will release an additional in-depth analysis, including aspects related to ADMAN firms’ revenues, age and size, and will offer an outlook of the distribution across industrial ecosystems.
Background
The study builds on the recommendations of the Industrial Forum’s Task Force on Advanced Manufacturing. The results were first released on 16 April 2024 at the Advanced Manufacturing Industry Conference hosted by the European Commission’s DG GROW. The conference gathered various public and private stakeholders to discuss challenges and opportunities faced by the advanced manufacturing industry.
The analysis is based on the well-known DGTES (Digital Techno-Economic Ecosystems) methodology developed by the JRC’s digital economy leading scientists. DGTES is primarily a policy-relevant analytical tool functional to analyse EU digital transition. By combining different data sources of digital ecosystems into an extensive database, it gives an overview of the critical elements of the digital ecosystem, such as players, activities, and interlinkages.
Details
- Publication date
- 2 July 2024
- Author
- Joint Research Centre
- JRC portfolios