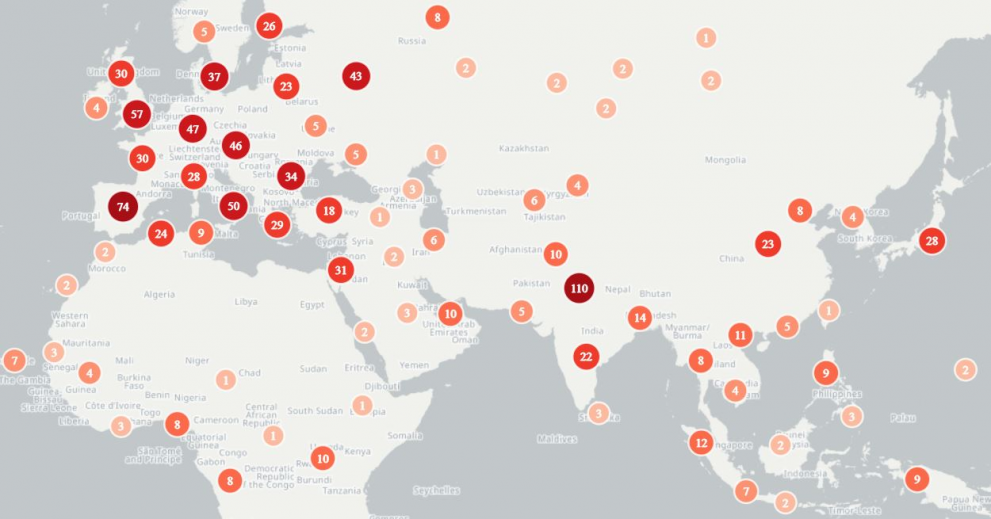
This media surveillance collects articles reported through publicly available web sites.
It is created with the Europe Media Monitor (EMM).
The selection and placement of stories are determined automatically by a computer program.
Headlines
- India’s total COVID-19 cases passed 18 million on Thursday while vaccine drive is slowing down
- Israel: Indian COVID-19 strain spreads in Israel, also among vaccinated; children from five schools among Israel’s 41 cases of Indian COVID-19 strain
- Brazil nears 400,000 COVID-19 deaths while India has become the country with the second highest number of cases after the US
- US vaccination pace slides further from peak levels as COVID-19 case counts decline in most states
- EU warned about Russia’s and China’s efforts to discredit Western COVID-19 vaccines
- Spain: nearly half of 60-69 age group have received at least one shot
- Portugal detected six cases of Indian variant
- France will start relaxing a nightly curfew and allow cafes, bars and restaurants to offer outside service from May 19
- Germany gives record 1.1 million COVID-19 shots as cases ease
- Denmark delays decision over use of Johnson & Johnson vaccine
- Belgium: decline in COVID-19 cases in schools after Easter break
- Italy extends COVID-19 travel ban to Bangladesh and Sri Lanka as well as India
- Romania detects first case of variant found in India
- Luxembourg: cluster of cases among students following private party
- New Zealand reported three new cases in managed isolation
- China's Zhejiang Province reported 11 imported confirmed COVID-19 cases and one imported asymptomatic carrier
- Japan: new infections in Tokyo top 1,000 for first time since 28 January; Tokyo Olympic Games organizers lay out updated athlete virus countermeasures
The following news were found among the most mentioned/retweeted items:
- "Yogi orders crack down on hospitals flagging oxygen shortage" (telegraphindia)
- "85-year-old COVID-positive RSS Swayamsevak gave up his bed and life so another person can live" (opindia)
- "The document confirming that Pfizer offered the government the vaccines against the coronavirus in advance" (tn)
- "Greece and Italy lower taxes while Sánchez 'massacres' taxpayers, Spain's fiscal policy also collides with the tax cuts in Portugal or Germany" (libremercado)
- "Biden's move to share vaccine doses could be a global game changer" (axios)
The hashtags #india and #oxygen were trending due to reports of oxygen shortages in Indian hospitals.
The most mentioned English sources were the Telegraph India, OP India, India Today, the Washington Post and the New York Times.
TN Argentina, Infobae, Eldiario and Eldestapeweb, and Francetvinfo and 20minutes were among the most mentioned Spanish and French sources, respectively.
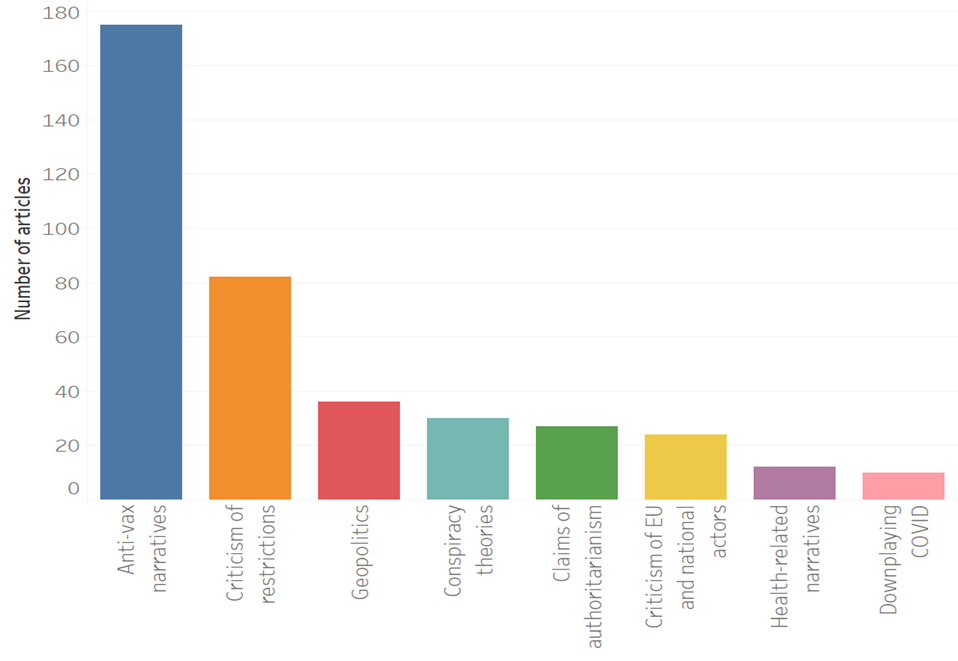
Misinformation
396 articles from unverified sources were selected forming 8 supernarratives over the last week:
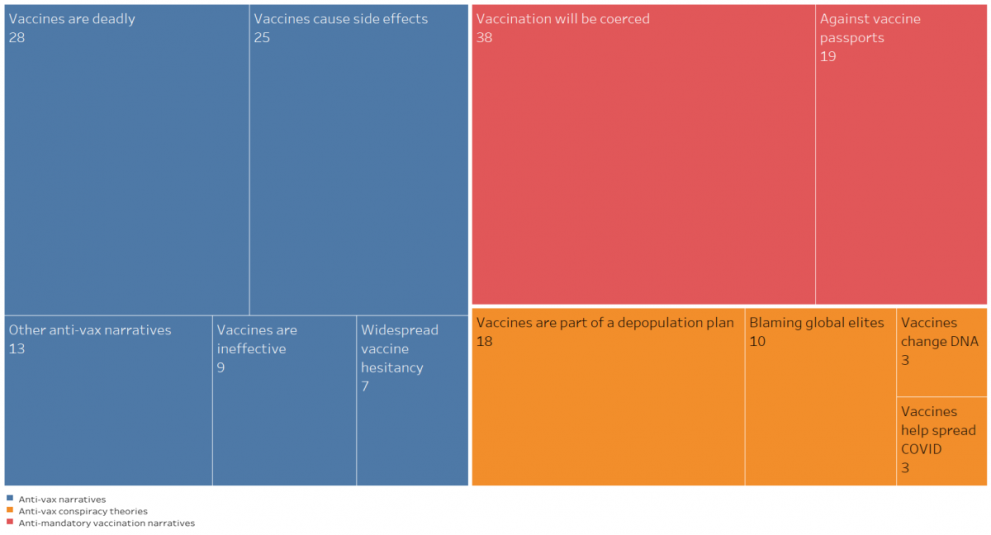
The treemap shows the narratives and subnarratives associated with anti-vax articles. The colours represent the narratives, while the text indicates each subnarrative. The bigger the size of the box, the higher the number of articles tagged as that narrative and subnarrative.
Fact Check
- Fact checkers debunk claims that according to the US Food and Drug Administration, the first vaccine dose correlates with increased COVID-19 infections, clarifying that the FDA document the claims seem to be based upon states that vaccine recipients might develop side effects that appear similar to COVID-19 symptoms, not COVID-19 infections (usatoday).
- Fact checkers debunk claims that you can get side effects of COVID-19 vaccines simply by being in close proximity to someone who has had the vaccine, reporting that there is nothing in COVID-19 vaccines that could cause vaccine shedding (fullfact).
- Fact checkers address claims that COVID-19 vaccines cause herpes, reporting that the study the claims are based upon “raises awareness to a potential causal link” between COVID-19 vaccination and herpes, but does not prove causality (snopes).
Download PDF
Contact
Mail to JRC-EMM-SUPPORT ec [dot] europa [dot] eu (subject: COVID-19%20media%20surveillance) (JRC-EMM-SUPPORT[at]ec[dot]europa[dot]eu)
ec [dot] europa [dot] eu (subject: COVID-19%20media%20surveillance) (JRC-EMM-SUPPORT[at]ec[dot]europa[dot]eu)
Related Content
Details
- Publication date
- 29 April 2021
