
JRC scientists have developed methods for the in-depth characterization of multi-functionalized gold nanoparticles. This will support the development of advanced nanomaterials for health applications.
Multi-functionalized nanoparticles are of great interest for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. However, at the moment the characterization of complex, multifunctional nanoparticles is still challenging and this hampers the development of these advanced materials for health applications.
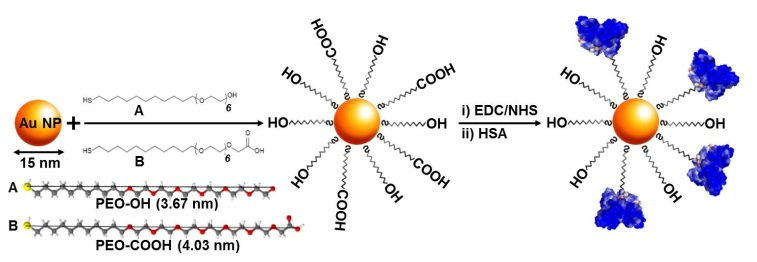
A new JRC publication – in close collaboration with researchers from Diamond Light Source (Synchrotron Radiation Facility, UK) – provides a suite of analytical methods for the systematic characterization and understanding on the surface functionalization of these complex systems.
A combination of techniques was applied to rationally designed gold nanoparticles to measure protein adsorption and protein binding, namely:
- Centrifugal Liquid Sedimentation
- Dynamic Light Scattering
- Flow Field Fractionation
- Transmission Electron Microscopy
- Circular Dichroism
This in-depth characterization will support the development of advanced nanomaterials for health applications.
Read more in: I. Ojea-Jiménez et al. Rational design of multi-functional gold nanoparticles with controlled biomolecule adsorption: a multi-method approach for in-depth characterization, Nanoscale 10, 10173-10181 (2018); doi: 10.1039/c8nr00973b
Related Content
Details
- Publication date
- 17 July 2018
